Thymectomy
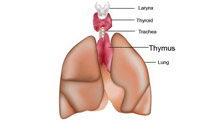
Thymus is immediately beneath the breastbone at the level of the heart. The thymus processes a type of white blood cell known as a T-lymphocyte which govern cellular immunity. These help cells recognize and destroy invading bacteria, virus, etc., abnormal cell growth such as cancer. Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a type of autoimmune disorders. An autoimmune disorder occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. In people with MG, the body produces antibodies that block the muscle cells from receiving messages from the nerve cell. The muscle weakness can lead to a variety of symptoms include breathing difficulty, swallowing difficulty, difficulty climbing stairs and talking, drooping head, facial paralysis, fatigue, hoarseness, double vision, and eyelid drooping.
In some cases, MG may be associated with tumors of the thymus. Surgery to remove the thymus (thymectomy) is necessary especially when there is a tumor present for treatment. Minimally invasive thymectomy is a new technique with one or two small incision on the throat.
